Measuring AML Software Effectiveness: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)

Money laundering poses a significant and ongoing threat to the global financial system, undermining the integrity and stability of financial institutions across the world. This practice involves disguising the origins of illegally obtained funds to make them appear legitimate, thereby jeopardising financial systems and contributing to a range of criminal activities. To effectively combat this issue, organisations must implement advanced Anti-Money Laundering (AML) software. This technology is designed to identify, detect, and prevent money laundering activities through sophisticated algorithms and automated processes.
However, deploying AML software alone is not enough. Financial institutions must also focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the effectiveness of their AML systems. KPIs provide critical insights into how well the software is performing in its role—measuring aspects such as the accuracy of suspicious activity alerts, the efficiency of transaction monitoring, and the overall impact on regulatory compliance. By systematically tracking and analysing these metrics, organisations can ensure their AML software is operating at peak efficiency, effectively mitigating financial crime, and maintaining the integrity of their operations. This approach helps institutions not only stay ahead of evolving threats but also meet stringent regulatory requirements and protect their reputation in the global financial landscape.
The Role of AML Software
AML software is crucial for financial institutions, designed to prevent, detect, and report money laundering activities. It automates complex processes such as customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, risk assessment, and record-keeping, helping institutions navigate the challenges of financial crime prevention.
Understanding KPIs in AML Software
To evaluate the effectiveness of AML software, organisations should track and analyse various KPIs. These metrics provide insights into the performance of the AML system, highlighting successes and identifying areas for improvement.
Key AML KPIs include:
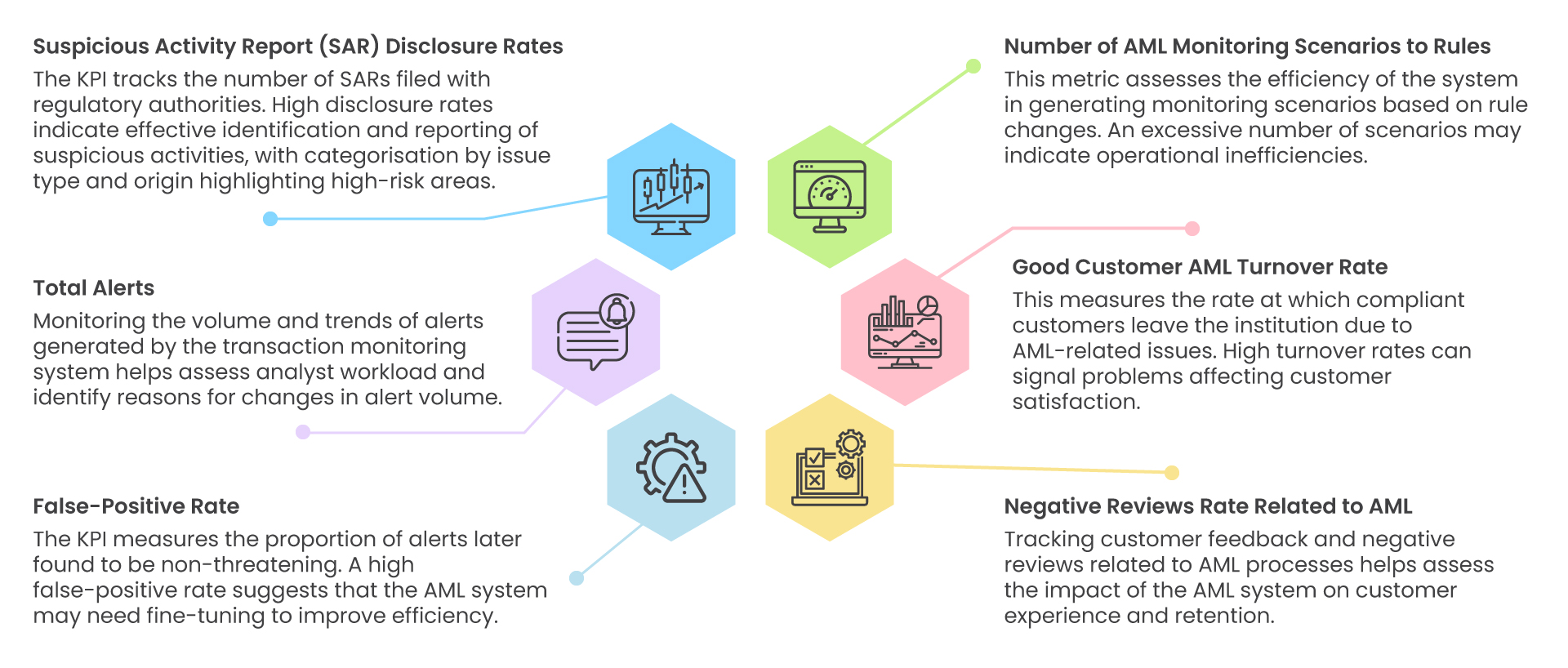
- Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) Disclosure Rates:
The KPI tracks the number of SARs filed with regulatory authorities. High disclosure rates indicate effective identification and reporting of suspicious activities, with categorisation by issue type and origin highlighting high-risk areas.
- Total Alerts:
Monitoring the volume and trends of alerts generated by the transaction monitoring system helps assess analyst workload and identify reasons for changes in alert volume.
- False-Positive Rate:
The KPI measures the proportion of alerts later found to be non-threatening. A high false-positive rate suggests that the AML system may need fine-tuning to improve efficiency.
- Number of AML Monitoring Scenarios to Rules:
This metric assesses the efficiency of the system in generating monitoring scenarios based on rule changes. An excessive number of scenarios may indicate operational inefficiencies.
- Good Customer AML Turnover Rate:
This measures the rate at which compliant customers leave the institution due to AML-related issues. High turnover rates can signal problems affecting customer satisfaction.
- Negative Reviews Rate Related to AML:
Tracking customer feedback and negative reviews related to AML processes helps assess the impact of the AML system on customer experience and retention.
Importance of KPIs in Measuring AML Software Effectiveness
KPIs are crucial for evaluating AML software effectiveness by:
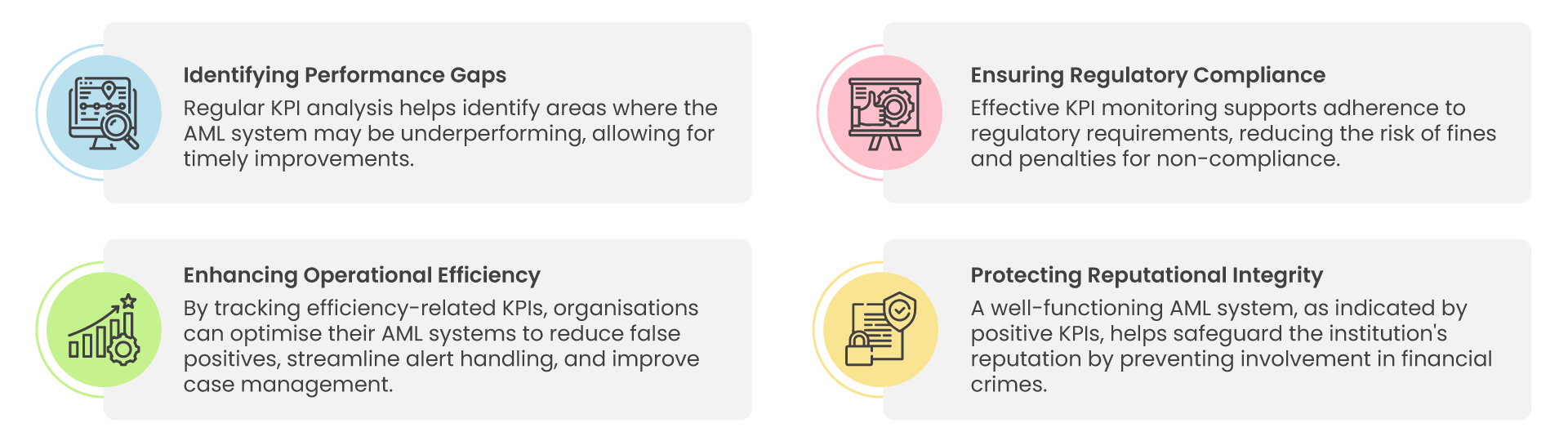
- Identifying Performance Gaps:
Regular KPI analysis helps identify areas where the AML system may be underperforming, allowing for timely improvements.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency:
By tracking efficiency-related KPIs, organisations can optimise their AML systems to reduce false positives, streamline alert handling, and improve case management.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
Effective KPI monitoring supports adherence to regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties for non-compliance.
- Protecting Reputational Integrity:
A well-functioning AML system, as indicated by positive KPIs, helps safeguard the institution’s reputation by preventing involvement in financial crimes.
Global Perspective on AML Software
For global banks and financial institutions, AML software must address diverse regulatory environments and the complexities of cross-border transactions. Effective AML software facilitates:

- Compliance Across Jurisdictions
Different countries and regions have their own specific AML regulations and compliance standards. For multinational banks and financial institutions, ensuring compliance with these varied requirements is a daunting task. AML software provides a comprehensive solution by incorporating international compliance standards, such as those set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), ensuring that institutions remain compliant across multiple jurisdictions. This includes generating Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) accurately and efficiently, tailored to the specific regulatory requirements of each country.
- Streamlined Customer Onboarding
Global operations involve dealing with a diverse customer base, each with unique regulatory requirements for onboarding and due diligence. AML software streamlines the customer onboarding process through automation of identity verification and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures a consistent and compliant onboarding experience across different regions, reducing the risk of regulatory breaches.
- Enhanced Transaction Monitoring
Cross-border transactions adds another layer of complexity to AML efforts. AML software enhances transaction monitoring by employing reliable detection models that can flag unusual activities in real-time. These models are designed to adapt to different transaction patterns and regulatory requirements, providing a robust defense against money laundering activities regardless of the transaction’s origin or destination.
- Risk Mitigation in Global Operations
AML software plays a crucial role in mitigating risks associated with global financial operations. By continuously assessing and analysing transaction data, the software helps institutions identify and respond to potential money laundering threats promptly. This proactive approach is vital in maintaining the financial stability and integrity of institutions operating in multiple countries.
- Efficient Record-Keeping and Reporting
Maintaining accurate and detailed records is a cornerstone of AML compliance. Global financial institutions must adhere to various record-keeping requirements, which can vary significantly between jurisdictions. AML software provides a centralised and easily accessible storage facility for meticulous records of customers, transactions, and due diligence activities. This ensures seamless compliance with diverse regulatory stipulations and simplifies the auditing process.
- Adaptability to Evolving Threat
The threat landscape for money laundering is constantly evolving, with new techniques and methods emerging regularly. AML software must be adaptable and scalable to keep pace with these changes. Advanced AML solutions incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence to continuously update and refine detection models, ensuring that institutions can effectively combat new and emerging threats.
- Integration with Global Financial Systems
Global financial institutions often operate with a multitude of financial systems and platforms. AML software must integrate seamlessly with these existing systems to provide a unified approach to compliance and risk management. This integration ensures that all aspects of the institution’s operations are covered, from transaction monitoring to customer due diligence, providing a holistic view of potential risks and compliance issues.
- Enhancing Global Collaboration
Effective AML efforts require collaboration and information sharing between institutions and regulatory bodies worldwide. AML software facilitates this collaboration by providing secure and efficient channels for sharing relevant data and insights. This enhances the overall effectiveness of global AML efforts and helps build a more resilient financial system.
In the ongoing fight against money laundering, leveraging robust AML software and monitoring relevant KPIs is essential for global banks and financial institutions. By focusing on these key metrics, organisations can ensure their AML systems are effective, efficient, and capable of safeguarding financial integrity. Investing in advanced AML technology and continuously evaluating its performance through KPIs will protect against financial crime and enhance operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.

Money laundering poses a significant and ongoing threat to the global financial system, undermining the integrity and stability of financial institutions across the world. This practice involves disguising the origins of illegally obtained funds to make them appear legitimate, thereby jeopardising financial systems and contributing to a range of criminal activities. To effectively combat this issue, organisations must implement advanced Anti-Money Laundering (AML) software. This technology is designed to identify, detect, and prevent money laundering activities through sophisticated algorithms and automated processes.
However, deploying AML software alone is not enough. Financial institutions must also focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the effectiveness of their AML systems. KPIs provide critical insights into how well the software is performing in its role—measuring aspects such as the accuracy of suspicious activity alerts, the efficiency of transaction monitoring, and the overall impact on regulatory compliance. By systematically tracking and analysing these metrics, organisations can ensure their AML software is operating at peak efficiency, effectively mitigating financial crime, and maintaining the integrity of their operations. This approach helps institutions not only stay ahead of evolving threats but also meet stringent regulatory requirements and protect their reputation in the global financial landscape.
The Role of AML Software
AML software is crucial for financial institutions, designed to prevent, detect, and report money laundering activities. It automates complex processes such as customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, risk assessment, and record-keeping, helping institutions navigate the challenges of financial crime prevention.
Understanding KPIs in AML Software
To evaluate the effectiveness of AML software, organisations should track and analyse various KPIs. These metrics provide insights into the performance of the AML system, highlighting successes and identifying areas for improvement.
Key AML KPIs include:

- Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) Disclosure Rates:
The KPI tracks the number of SARs filed with regulatory authorities. High disclosure rates indicate effective identification and reporting of suspicious activities, with categorisation by issue type and origin highlighting high-risk areas.
- Total Alerts:
Monitoring the volume and trends of alerts generated by the transaction monitoring system helps assess analyst workload and identify reasons for changes in alert volume.
- False-Positive Rate:
The KPI measures the proportion of alerts later found to be non-threatening. A high false-positive rate suggests that the AML system may need fine-tuning to improve efficiency.
- Number of AML Monitoring Scenarios to Rules:
This metric assesses the efficiency of the system in generating monitoring scenarios based on rule changes. An excessive number of scenarios may indicate operational inefficiencies.
- Good Customer AML Turnover Rate:
This measures the rate at which compliant customers leave the institution due to AML-related issues. High turnover rates can signal problems affecting customer satisfaction.
- Negative Reviews Rate Related to AML:
Tracking customer feedback and negative reviews related to AML processes helps assess the impact of the AML system on customer experience and retention.
Importance of KPIs in Measuring AML Software Effectiveness
KPIs are crucial for evaluating AML software effectiveness by:

- Identifying Performance Gaps:
Regular KPI analysis helps identify areas where the AML system may be underperforming, allowing for timely improvements.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency:
By tracking efficiency-related KPIs, organisations can optimise their AML systems to reduce false positives, streamline alert handling, and improve case management.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
Effective KPI monitoring supports adherence to regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties for non-compliance.
- Protecting Reputational Integrity:
A well-functioning AML system, as indicated by positive KPIs, helps safeguard the institution’s reputation by preventing involvement in financial crimes.
Global Perspective on AML Software
For global banks and financial institutions, AML software must address diverse regulatory environments and the complexities of cross-border transactions. Effective AML software facilitates:

- Compliance Across Jurisdictions
Different countries and regions have their own specific AML regulations and compliance standards. For multinational banks and financial institutions, ensuring compliance with these varied requirements is a daunting task. AML software provides a comprehensive solution by incorporating international compliance standards, such as those set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), ensuring that institutions remain compliant across multiple jurisdictions. This includes generating Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) accurately and efficiently, tailored to the specific regulatory requirements of each country.
- Streamlined Customer Onboarding
Global operations involve dealing with a diverse customer base, each with unique regulatory requirements for onboarding and due diligence. AML software streamlines the customer onboarding process through automation of identity verification and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures a consistent and compliant onboarding experience across different regions, reducing the risk of regulatory breaches.
- Enhanced Transaction Monitoring
Cross-border transactions adds another layer of complexity to AML efforts. AML software enhances transaction monitoring by employing reliable detection models that can flag unusual activities in real-time. These models are designed to adapt to different transaction patterns and regulatory requirements, providing a robust defense against money laundering activities regardless of the transaction’s origin or destination.
- Risk Mitigation in Global Operations
AML software plays a crucial role in mitigating risks associated with global financial operations. By continuously assessing and analysing transaction data, the software helps institutions identify and respond to potential money laundering threats promptly. This proactive approach is vital in maintaining the financial stability and integrity of institutions operating in multiple countries.
- Efficient Record-Keeping and Reporting
Maintaining accurate and detailed records is a cornerstone of AML compliance. Global financial institutions must adhere to various record-keeping requirements, which can vary significantly between jurisdictions. AML software provides a centralised and easily accessible storage facility for meticulous records of customers, transactions, and due diligence activities. This ensures seamless compliance with diverse regulatory stipulations and simplifies the auditing process.
- Adaptability to Evolving Threat
The threat landscape for money laundering is constantly evolving, with new techniques and methods emerging regularly. AML software must be adaptable and scalable to keep pace with these changes. Advanced AML solutions incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence to continuously update and refine detection models, ensuring that institutions can effectively combat new and emerging threats.
- Integration with Global Financial Systems
Global financial institutions often operate with a multitude of financial systems and platforms. AML software must integrate seamlessly with these existing systems to provide a unified approach to compliance and risk management. This integration ensures that all aspects of the institution’s operations are covered, from transaction monitoring to customer due diligence, providing a holistic view of potential risks and compliance issues.
- Enhancing Global Collaboration
Effective AML efforts require collaboration and information sharing between institutions and regulatory bodies worldwide. AML software facilitates this collaboration by providing secure and efficient channels for sharing relevant data and insights. This enhances the overall effectiveness of global AML efforts and helps build a more resilient financial system.
In the ongoing fight against money laundering, leveraging robust AML software and monitoring relevant KPIs is essential for global banks and financial institutions. By focusing on these key metrics, organisations can ensure their AML systems are effective, efficient, and capable of safeguarding financial integrity. Investing in advanced AML technology and continuously evaluating its performance through KPIs will protect against financial crime and enhance operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
