Time to Bridge the Gap between Consumers & Financial Services with Embedded Finance

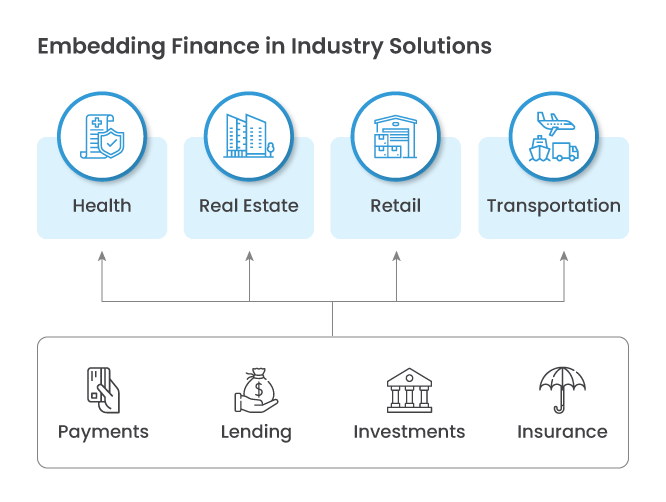
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the integration of financial products into everyday digital interfaces has revolutionised the way consumers and businesses interact with financial services. This phenomenon, known as Embedded Finance, has unlocked a myriad of possibilities across various sectors, from customer loyalty apps to digital wallets, accounting software, and shopping-cart platforms.
Embedded Finance seamlessly integrates financial services into nonfinancial customer experiences, making acquiring financial products a natural extension of daily activities. This evolution has been fuelled by fundamental changes in commerce, merchant and consumer behaviour, and technology, particularly the digitalisation of commerce and business management.
UPI’s Dominance in India’s Payment Landscape
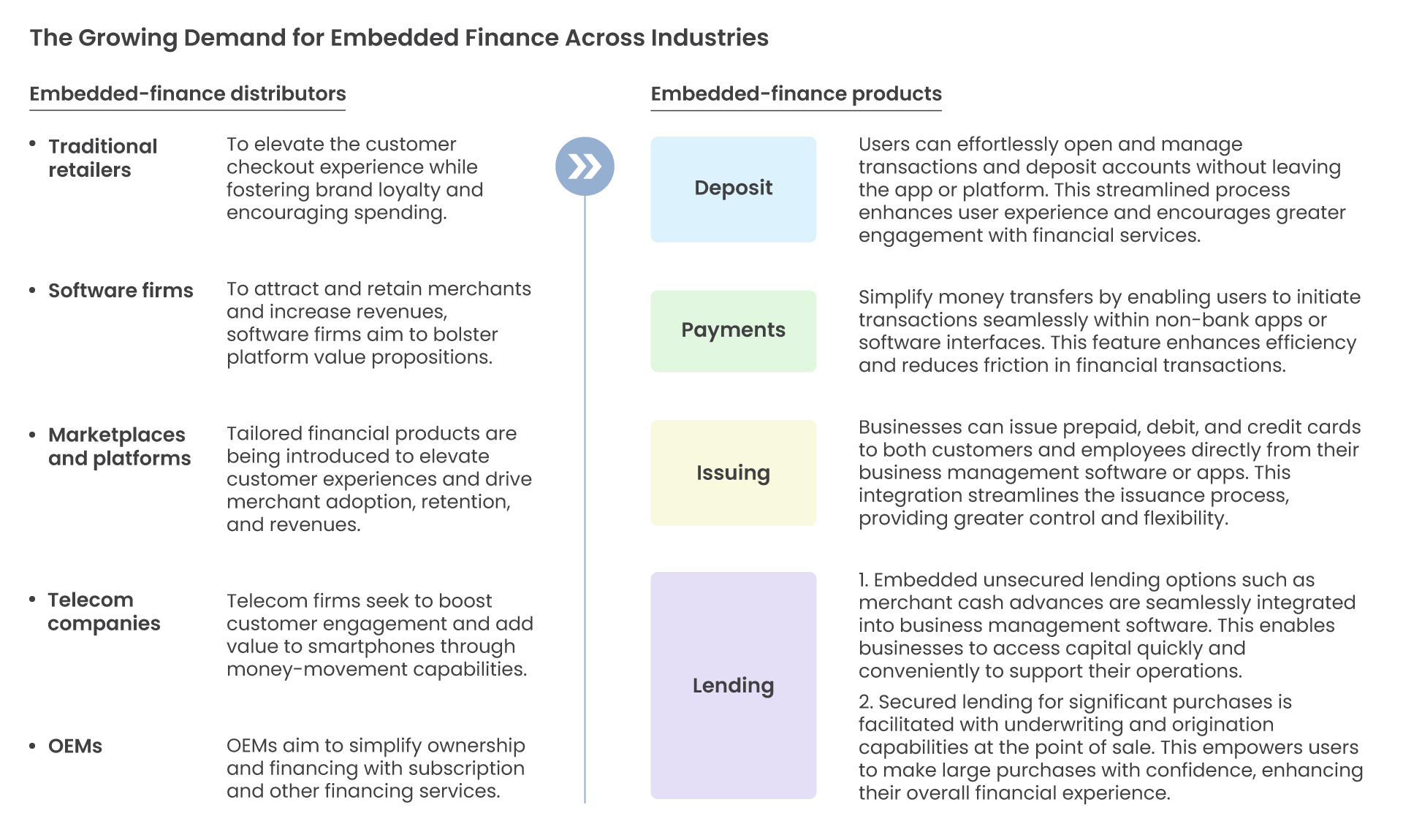
Companies across industries are recognising the potential of Embedded Finance to better serve both business and consumer segments. By offering a diverse range of financial instruments through API-based distribution, manufacturers can tap into a larger customer base while also accessing financial products or services as needed.
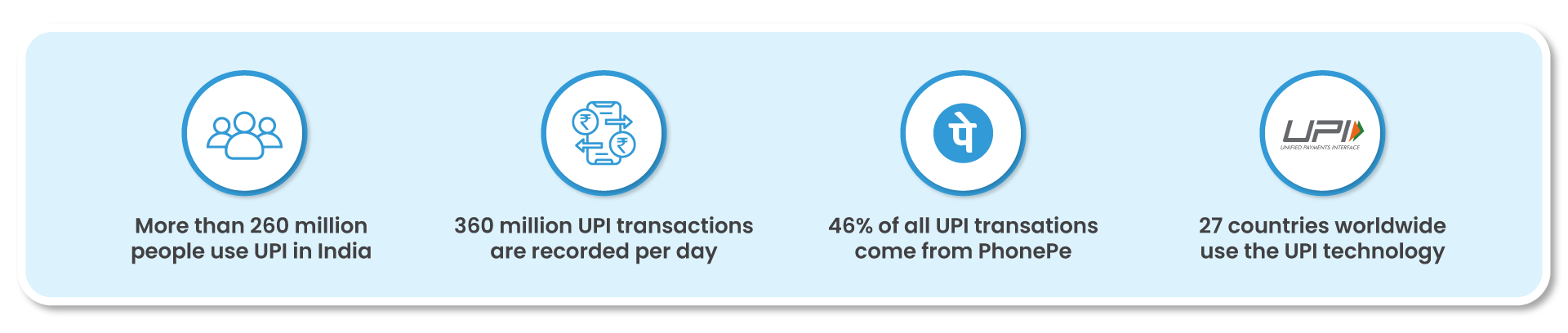
One of the most notable examples of Embedded Finance’s impact is seen in the rise of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India. With billions of transactions worth trillions of rupees recorded monthly, UPI has become a dominant force in the country’s payment ecosystem, replacing cash and driving digitisation of the economy. The acceptance of UPI among merchants has also increased, enhancing credit eligibility for small businesses and consumers.
Future Growth and Innovation in Embedded Finance
Embedded Finance holds the key to bringing millions of Indians into the mainstream financial system, providing access to savings, credit, and insurance products. By leveraging technology, fast and hassle-free access to financial services is made possible, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and closing the gap between financial services and end consumers.
The banking industry, traditionally known for its complexity and regulation, is also embracing emerging technologies to enhance customer experience. Global banks are exploring immersive technologies to enable banking through entertainment channels, while in India, Punjab National Bank and Bank of Maharashtra have introduced a 3D Virtual Lounge to provide customers with interactive banking experiences. KiyaAI’s Kiyaverse platform further empowers banks with immersive products and services, signalling a shift towards innovation and customer-centricity in the banking sector.
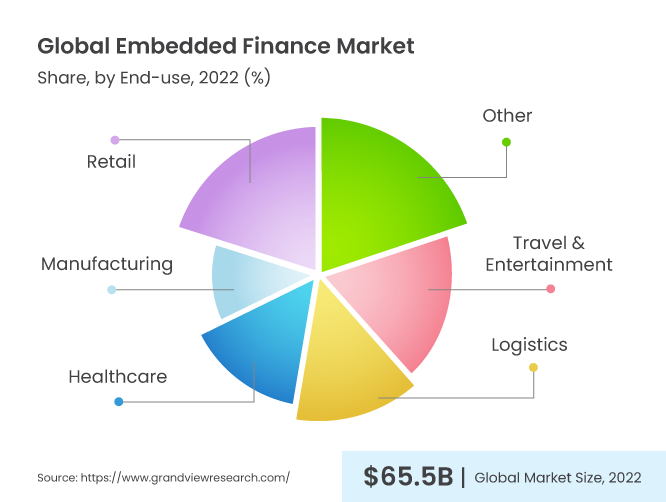
As non-traditional players continue to enter the fintech space, the adoption of Embedded Finance is expected to grow significantly, offering new opportunities for direct-to-consumer (D2C)Â companies to disrupt the financial services industry. With technology as the driving force, Embedded Finance is bridging the gap between consumers and financial services, paving the way for a more inclusive and accessible financial ecosystem.

In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the integration of financial products into everyday digital interfaces has revolutionised the way consumers and businesses interact with financial services. This phenomenon, known as Embedded Finance, has unlocked a myriad of possibilities across various sectors, from customer loyalty apps to digital wallets, accounting software, and shopping-cart platforms.
Embedded Finance seamlessly integrates financial services into nonfinancial customer experiences, making acquiring financial products a natural extension of daily activities. This evolution has been fuelled by fundamental changes in commerce, merchant and consumer behaviour, and technology, particularly the digitalisation of commerce and business management.



UPI’s Dominance in India’s Payment Landscape
Companies across industries are recognising the potential of Embedded Finance to better serve both business and consumer segments. By offering a diverse range of financial instruments through API-based distribution, manufacturers can tap into a larger customer base while also accessing financial products or services as needed.
One of the most notable examples of Embedded Finance’s impact is seen in the rise of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India. With billions of transactions worth trillions of rupees recorded monthly, UPI has become a dominant force in the country’s payment ecosystem, replacing cash and driving digitisation of the economy. The acceptance of UPI among merchants has also increased, enhancing credit eligibility for small businesses and consumers.

Future Growth and Innovation in Embedded Finance
Embedded Finance holds the key to bringing millions of Indians into the mainstream financial system, providing access to savings, credit, and insurance products. By leveraging technology, fast and hassle-free access to financial services is made possible, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and closing the gap between financial services and end consumers.
The banking industry, traditionally known for its complexity and regulation, is also embracing emerging technologies to enhance customer experience. Global banks are exploring immersive technologies to enable banking through entertainment channels, while in India, Punjab National Bank and Bank of Maharashtra have introduced a 3D Virtual Lounge to provide customers with interactive banking experiences. KiyaAI’s Kiyaverse platform further empowers banks with immersive products and services, signalling a shift towards innovation and customer-centricity in the banking sector.
As non-traditional players continue to enter the fintech space, the adoption of Embedded Finance is expected to grow significantly, offering new opportunities for direct-to-consumer (D2C)Â companies to disrupt the financial services industry. With technology as the driving force, Embedded Finance is bridging the gap between consumers and financial services, paving the way for a more inclusive and accessible financial ecosystem.
